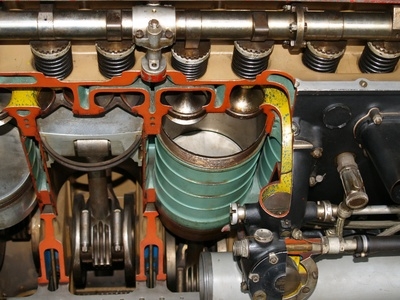
Engine valves are portholes that control the flow of gases into and out of an engine. They are usually located in the top of an engine's combustion chamber and open and close by means of a mechanical cam that controls the timing and duration of their movement according to desired engine speed.
Intake valves control the flow of the fuel and air into the combustion chamber. The intake valve opens on the intake stroke of the engine and closes after the chamber has filled. This happens in a fraction of a second.
Exhaust valves allow the expulsion of the burned fuel-and-air mixture, as exhaust gases, out of the combustion chamber. Exhaust valves open during the exhaust stroke and close again before the intake stroke just as quickly as the intake valves did.
Both intake and exhaust valves are closed to seal the combustion chamber during compression and ignition of the fuel-and-air mixture.
With the valves still closed, ignition of the fuel-and-air mix in the combustion chamber causes the pressure of exploding gases to force the piston downward, transferring the energy of the combustion process to the engine's crankshaft.
Exhaust valves are typically 20 percent smaller than intake valves due the reduced volume of the burned fuel-and-air mixture. The burned exhaust gas requires less area to escape through.
Exhaust valves experience more heat due to hot exhaust gases flowing through them on the exhaust stroke, making them more likely to experience wear and damage.