
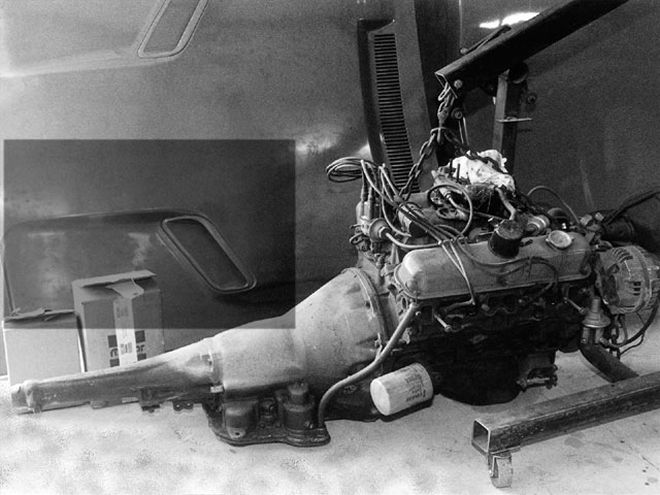
 Tony had this 340 engine at his shop. It's an unmolested survivor that was pulled from a rough, low-mileage '71 E-Body. Finding the proper, correct carburetor for your project entails some searching and the knowledge of which unit or units fit your application.
Tony had this 340 engine at his shop. It's an unmolested survivor that was pulled from a rough, low-mileage '71 E-Body. Finding the proper, correct carburetor for your project entails some searching and the knowledge of which unit or units fit your application.
This month, we're pleased to introduce a new series of articles using information compiled by Tony D'Agostino of Tony's Parts in Harrington, Delaware. As you may already know, Tony is a major supplier of both N.O.S. and used Chrysler vehicle parts and equipment to the hobby. This Treasure Hunt series will focus on items commonly found in junk piles, swap meets, and dusty corners of garages. For this introduction, we'll look at carburetors used on Chrysler performance cars during the '60s and the early '70s.
Other than the optional fuel-injection systems used on a handful of luxury models, every performance car Chrysler created used four-barrel, six-barrel, or eight-barrel induction systems. While most of us know what a carburetor looks like, it can be hard to determine which models originally came on our cars. This Treasure Hunt will help you identify carburetors when searching through piles of other rubble.
The most important and easiest way to tell Mopar-specific carbs from those offered by other manufacturers is the throttle-stud bracket shape. This bracket is located on the driver side of the carb where the throttle stud screws into the bracket; its shape and design is unique to the Chrysler family, whether the carb was made by Carter or by Holley
The Carter Connection
The most common four-barrel carb found on Chryslers during the '60s era were manufactured by Carter and came in two specific designs: the AFB (Aluminum Four Barrel) and the AVS (Air Valve Secondary). From a distance, the two look virtually identical; both are box-like in shape and use a quadrant of evenly or almost evenly sized barrels when viewed from the bottom.
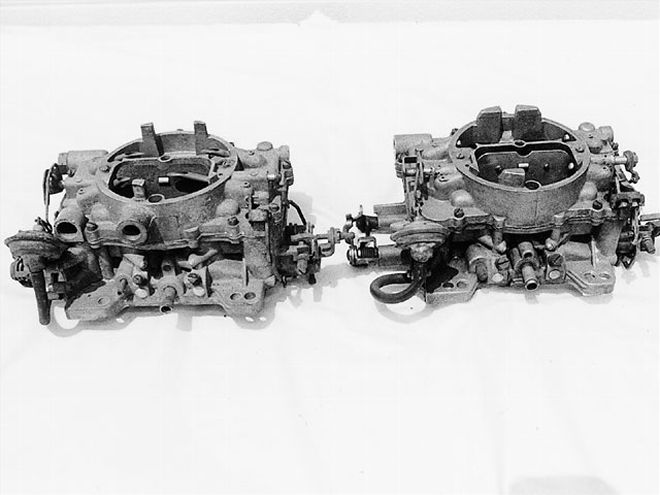
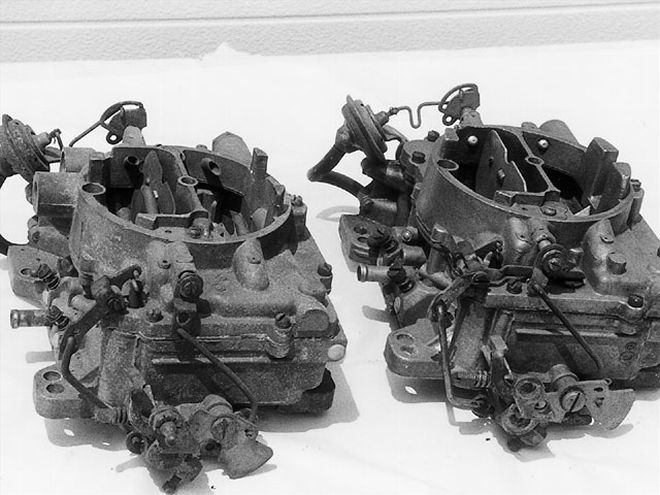 <strong>AFB</strong><br>Here are a pair of AFB carbs from a Hemi motor, which used these units exclusively from 1966 to 1971 in street applications. Modified twin AFBs were used on the '67 WO/RO cars as well. After the WCFB was discontinued, the single AFB was the standard carb on Chrysler performance models until the debut of the AVS in 1968. The specific date code and four-digit part number on both the AFB and the AVS models are easily visible in front of the passenger-side mounting flange.
<strong>AFB</strong><br>Here are a pair of AFB carbs from a Hemi motor, which used these units exclusively from 1966 to 1971 in street applications. Modified twin AFBs were used on the '67 WO/RO cars as well. After the WCFB was discontinued, the single AFB was the standard carb on Chrysler performance models until the debut of the AVS in 1968. The specific date code and four-digit part number on both the AFB and the AVS models are easily visible in front of the passenger-side mounting flange.
However, there are some significant differences. First, Carter cast the letters A F B or A V S into the housings located on the rear left corner, so this is a simple way to tell them apart. The AFB has the choke pull-off located high on the passenger side of the body, while the AVS is lower on the same side. The secondary flapper doors on the AFB consist of two plates mounted midway into each bore, while the AVS uses a single, large flapper door mounted to the top plate of the carb. In the AFB, this flapper system is operated using counterweights on either end of the flap-door shaft, while the AVS has an adjustable spring mounted to the flap-door shaft toward the driver side of the carb.
There are few other differences between them as well as major internal changes. The idle screws on the leading-edge base of the AFB were at 45-degree angles, while those on the AVS were mounted straight out. AVS carbs had only four mounting holes, while many AFBs had six or even eight mounting holes. Finally, the AFB uses a smaller flange on the carb-to-air cleaner-mounting area, except for the race carbs used on the '64 Max Wedges (PN 3705) and certain race Hemi models (PN 3861), which were of a larger top size.
There was a short progression from AFB to AVS because Carter brought out an even, more sizable carb called the ThermoQuad. This carb, of course, is easily identified by the large, black plastic centersection between the top and the bottom plate. It used a spread-bore design, with small primary and large secondary barrel openings when viewed from below. These carbs were used primarily on Mopar applications; most used examples probably came from a Chrysler vehicle. The biggest change during the course of this unit's production was the addition of a large solenoid built into the top plate of the ThermoQuad in the center rear. Since this occurred after 1975, these aren't considered musclecar-era units.
The Heads-up on Holley
In most instances, Chrysler used Carter, GM used Rochester, and Ford used Autolite and Motorcraft, but as the supercar era continued, they all turned to aftermarket supplier Holley Carburetors to provide carbs for their best models. Chrysler did so for most of the cross-ram-equipped, drag-race Hemi engines starting in mid-1964, then later on for 383- and 440-powered cars.
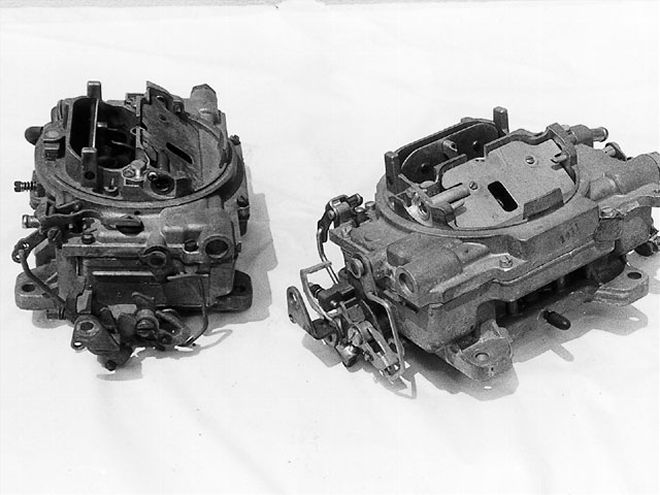 <strong>AVS</strong><br>The AVS design debuted on the new 340 and 383/335hp model of 1968 and would be the mainstay for the most popular years of the musclecar era. Externally, they differed from the AFB with top-mounted flapper doors, repositioned idle-mixture screws, and a lower-mounted choke cut-off, not to mention the letters A V S cast into the bowl area at the rear. Like the AFB, the date code and part number are located right in front of the passenger-side mounting flange.
<strong>AVS</strong><br>The AVS design debuted on the new 340 and 383/335hp model of 1968 and would be the mainstay for the most popular years of the musclecar era. Externally, they differed from the AFB with top-mounted flapper doors, repositioned idle-mixture screws, and a lower-mounted choke cut-off, not to mention the letters A V S cast into the bowl area at the rear. Like the AFB, the date code and part number are located right in front of the passenger-side mounting flange.
All of the OE Holley four-barrels used on factory Mopars were of the 4160 variety, using vacuum secondaries and a fuel balance tube that ran between the bowls on the driver side, with evenly sized barrel openings when viewed from the bottom. The easiest way to differentiate them from other Detroit versions is again the throttle-stud mounting bracket. The fuel line inlet is at a downward angle on the driver side as well. Other than that, they're similar to most others of that time.
In 1969 Chrysler selected Holley for the new triple two-barrel layout, commonly called the Six Pack after Dodge's slogan. These used the throttle-stud bracket specific to Chrysler on the primary (or center) carb; the secondaries have no metering blocks and large vacuum spring housings and all use a fuel line inlet located at a 45-degree downward angle on the passenger side.
Some Final Notes
This article is a basic introduction. There are several sources for additional information, primarily books published by Galen Govier's GTS company. These books come in a variety of pocket-size formats and are an invaluable source for those seeking date-code information and parts for specific model years. For servicing, performance, and emissions purposes, virtually every application used a different part number, creating literally dozens of numbers, despite simple physical interchangeability between models.
Parts for most Holley carburetors are still available, though some Carter models may be difficult to find small parts for. Don't overspend on models with heavy modifications for competition, which may require serious rebuilding. The Carter units are now being manufactured as a subsidiary of the Edelbrock performance line.
Carburetors were one of the most delicate and fragile parts on any car and subject to the corrosive effects of fuel. Any used carb should be rebuilt and checked thoroughly for leaks and damage before being put into service. Spilled gasoline on hot intake manifolds is a recipe for certain disaster.
Chase Chart-Chrysler CarbsCarter AFB single four-barrel1962318 poly, 361-B, 383-B, 413-RB1963361-B, 383-B, 413-RB1964273-A, 361-B, 383-B, 413-RB1965273-A, 383-B, 426W-RB 1966273-A, 383-B, 440-RB1967273-A, 383-B, 440-RB Carter AFB dual four-barrel inline1962413-RB ({{{300}}}-H) 1963413-RB (330-J)1964426-RB (330-K) 1966’71 426 Hemi Carter AFB dual four-barrel cross-ram(MW—Max Wedge by stage)1962413-RB (MW I)1963413-RB (MW I), 426-RB (MW II)1964426-RB (MW III), 426 Hemi (early) Carter AVS(available only in single four-barrel)1968340-A, 383-B, 440-RB1969340-A, 383-B, 440-RB1969340-A, 383-B, 440-RB1970340-A, 383-B, 440-RB1971383-B, 440-RB Carter ThermoQuad1971340-A, 383-B (off-road)1972340-A, 400-B1973360-A, 400-B, 440-RB1974360-A, 400-B, 440-RB Holley single four-barrel(440-RB ’67-’70 on C-Body models)1966273-A (D-Dart)1967440-RB1968440-RB1969383-B, 440-RB1970383-B, 440-RB1971383-B1972440-RB Holley dual four-barrel(drag race use packages—all cross-ram)1964426 Hemi1965426 Hemi1968426 Hemi Holley 3x2 Six Pack1969440-RB (A12)1970340-A (TA-SP), 440-RB1971440-RB1972440-RB