
 Archived Comparison
Archived Comparison
"Last year, observed and times by the Motor Industry Research Association, Reg Parnell demonstrated the ability of the DB4GT to go from 0 to 100 mph and back to 0 again in 24 seconds." —Car and Driver, June 1961
That sentence, which appeared 37 years ago in our report on the Aston Martin DB4GT, may not have been the first time that anyone ever quoted a 0-to-100-to-0 clocking, but it does establish the era in which this unique performance yardstick became popular.
By measuring a car's stopping power as well as its sheer acceleration, it was a straight-line test more acceptable to the sports-car world than the conventional, single-dimensional quarter-mile drag race. In 1965, Carroll Shelby took a shot at this test and claimed that his 427 Cobra did it in an astonishing 13.8 seconds—with Shelby driver Ken Miles at the wheel.
Others have continued to rely on this three-decades-old measure of performance, even as modern cars have become incomparably more powerful and capable than their Sixties counterparts. Now, with a new millennium in sight and numerous modified cars capable of topping 200 mph no farther away than your checkbook, we resolved to bring this historical measure of straight-line performance up to date with current technology and leave the 0-to-100-to-0 test to those mired in the past.
So we've simply added another 50 miles an hour to the moment when the C/D test driver removes his foot from the car's accelerator and stomps on the brake pedal. Although raising the test speed from 100 to 150 mph seems like a simple 50-percent increase, its effects are profound.
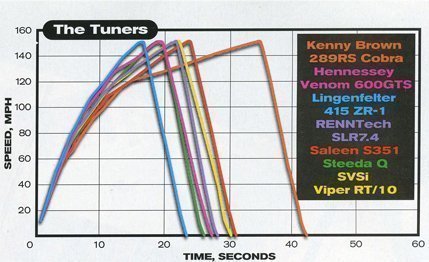

For one thing, overcoming the aerodynamic drag at 150 mph requires 3.38 times as much power as it does at 100 mph. Therefore, whereas acceleration at two-digit speeds is primarily determined by a vehicle's power-to-weight ratio, acceleration above 120 mph is limited more by the power-to-aerodynamic-drag ratio—the factor that also limits a vehicle's top speed.
Raising the peak speed from 100 to 150 mph also means that the brakes must dissipate 2.25 times as much energy while bringing the car to a complete stop. Moreover, it's done in one massive thermal jolt that's about twice as time-consuming as that produced by a stop from 100 mph.
To measure this performance, we employed our usual Datron DLS-1 optical fifth wheel coupled to an AEP-4 data logger. This is the most accurate test gear on the market, with roughly one-quarter the error margin found in radar-gun-based testing schemes. Besides, most commercial radar guns don't have sufficient range to conduct this test.
Our senior technical editor, Don Schroeder, was the test pilot. He was instructed to make sure that each and every run would exceed 150 mph because we would be accepting no near misses. Nor would we permit a piecing together of a car's best 0-to-150 acceleration time with its best 150-to-0 braking performance from a different run.
Tests were conducted on the 2.23-mile-long north-south straightaway at the Chrysler proving grounds in Chelsea, Michigan. Schroeder was to devote his first pass down the track to determining the best launch procedure, shifting strategy, and braking technique. That was followed by a cool-down run, and then the real thing: a full-speed 0-to-150-to-0 blast for the numbers.


Since the vehicles that we rounded up could complete the test in about a mile, Schroeder followed each run with a three-mile cool-down. That's how long it took to go to the end of the straight and return to the starting point.
We performed two runs in each direction and averaged the faster run each way. Those cars that were tricky to launch, shift, or stop without locking up wheels suffered the consequences. Anti-lock brakes were a major benefit because they allowed Schroeder to switch instantly from mashing the accelerator to full braking.
We collected two groups of cars. The more pulse-quickening collection consisted of modified, street-legal cars from seven of the most respected tuners in the country, with power outputs ranging from 450 to 640 horsepower and brakes and handling to match.
To avoid the remote possibility that any of our highly competitive entrants might deign to set up a one-trick special biased for this 0-to-150-to-0 test, a day earlier we wrung out the aftermarket cars on country roads and rated each one's real-world drivability with one to five stars, five being the best.
We also rounded up a group of seven fast factory-stock cars to establish some baseline numbers for this test. Finally, as if 15 cars were not enough to handle, we brought along a video crew from Speedvision, the cable racing network, to record this historic, high-speed flailing. The eye-opening results were to make their debut on Speedvision at 8 p.m. on Friday, July 10. For detailed results and specifications, turn the page.