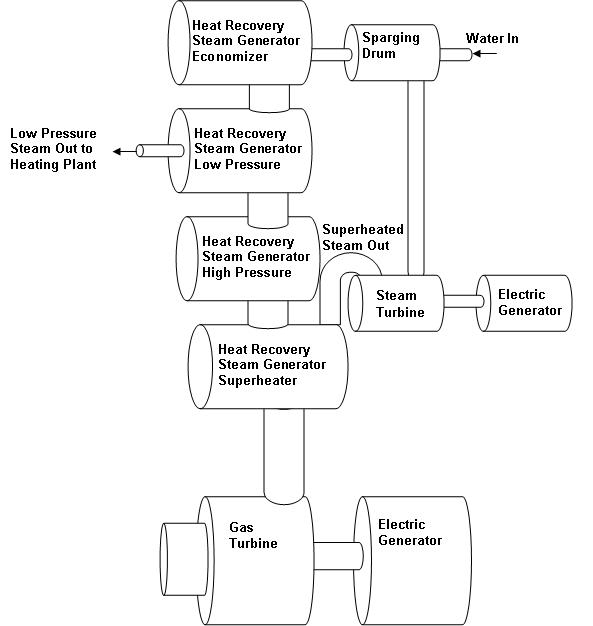
Heat recovery steam generators (HRSG), also formerly known as waste heat boilers or waste heat generators, use heat in the hot flue gas from one process operation to produce steam which is then used to power a different process operation. For example, their steam can be used to drive turbo-electric generators or in other energy intensive operations such as making paper. They harness the energy that used to be lost to the atmosphere through smokestacks to perform useful work. They have gained acceptance and popularity in industry as attention has been focused on rising energy costs and climate change.
Gas turbines are essentially jet engines driving large turbo generators instead of large aircraft. Their exhaust may contain substantial amounts of residual heat which used to be lost to the atmosphere. Multistage heat recovery steam generators suse the heat to produce superheated steam, high pressure steam, low pressure steam, and even hot water as the hot exhaust gradually loses its temperature.
The same process used for gas turbines can be put to work on large diesel engines used in co-generation. The diesel drives a generator for economical electricity production and then the hot exhaust can produce steam to drive another electrical generator or to provide heat for process operations as either steam or hot water.
The ideal goal of every multistage heat recovery steam generator is to effectively extract every BTU of heat that would exceed normal atmospheric temperature in the final effluent stream of gas, and put it to work either producing electricity or usable heat in another application such as hot water. Even using small amounts of heat to warm incoming cold water can result in substantial savings over the long term.
The production of syn-gas fuel from coal has several points with an excess of heat where a HRSG can be effective in providing energy savings.
HRSGs have found their way into many other types of process plants and chemical operations such as gaseous waste incinerators, spent solvent units, catalytic waste incinerators and power from burning byproducts such as bagasse, tree bark and trash incinerators. Any operations producing large amounts of heat as a byproduct are great candidates for HRSGs.