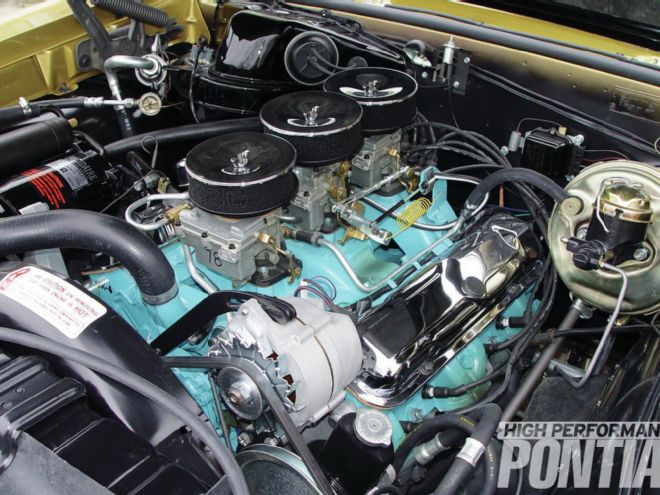

Last issue, we got up close and personal with Scott Tiemann’s 389 Tri-Power engine from the ’65 GTO his parents bought new at Detroit’s legendary Royal Pontiac. The car has always been in the Tiemann family, and Scott, one of the foremost Pontiac restorers, has not only known this engine from day one, but also pulled out all the stops to restore it.
We had the good fortune of photographing it when it was fresh from Scott’s Supercar Specialties shop and before it went back into the Tiemann-family GTO. If anybody knows how to make one of these vintage Tri-Power 389s look its Sunday best, it’s Scott. In fact, there was so much good stuff to show you that we couldn’t squeeze it all into one article. So here goes with Part 2. Last time, we left off with the timing marks, and now we pick up with the fan belts.
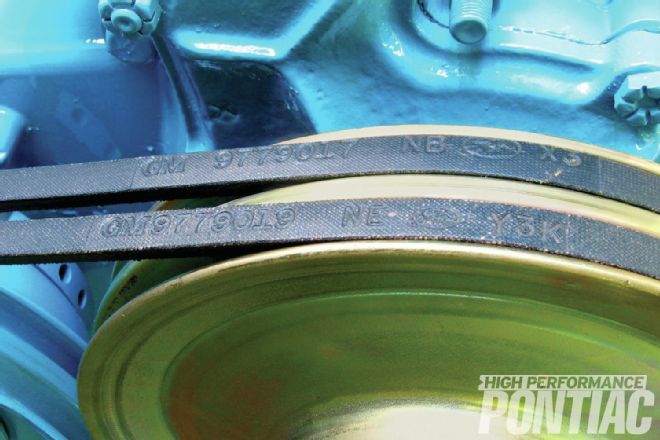
These are rare NOS fan belts. “They were brand-new in the GM package. I don’t know about the date code, but they are the correct part number and GM issue for this engine,” comments Scott. An easier-to-find alternative is a good reproduction that bears the right part numbers. “There’s a company called Quanta that’s making embossed-part-number fan belts that a lot of guys are getting—I’ve used plenty of them. You can use Quanta belts and get full points at the GTO Nationals,” says Scott.

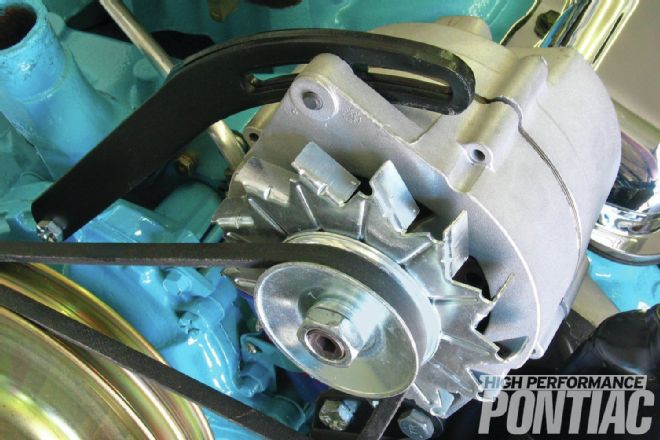
The alternator is a bare aluminum finish—not painted. The alternator pulley and fan are plated silver zinc.

If anybody knows how to make one of these vintage Tri-Power 389s look its Sunday best, it’s Scott
Bolts are silver-zinc plated except for the adjuster bolt, which is black phosphate. Alternator diodes, visible from the rear, are date-coded. This is a fine point, but it is something judges look at in higher levels of show judging. 4M15, the date code stamped on the center diode: 4=1964, M=December, 15=15th day of the month. 4M11, the code on the other two diodes, decodes similarly, but for the 11th day of the month.

The top alternator bracket is a compound bracket that fastens in two places with a silver self-locking nut on a blue stud for the rear bar, and a hardened silver bolt up front. Neither uses washers. The brackets are semigloss black.

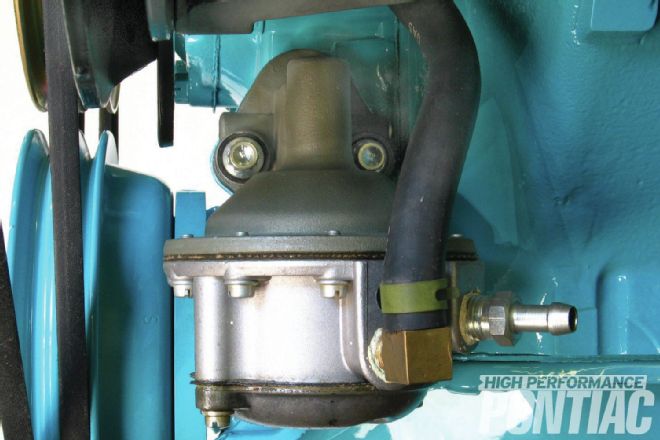
As with the water pump, the fuel pump’s rear bolt requires a special sealing washer because it extends into the timing cover. This is an NOS A/C fuel pump with its factory finish—the upper section is plated like a carburetor, the middle is bare aluminum. The bottom cover is also bare aluminum, but has discolored and appears darker. The outlet hose is printed with GAS in white letters, and the clamp is green. Up by the water pump, a blue NOS A/C fuel filter is mounted between the rubber and metal fuel lines. Green clamps are used there, too.

We’ve learned from examining original cars that they have the ‘X’ on them
At the base of the distributor is a metal band with part number 1111054 stamped into it (arrow). It’s an iron distributor with single points and is date coded for January 24, 1965. Iron distributors were used until ’67 or ’68, when Pontiac changed to aluminum. The hold down and bolt were originally bare steel, but were phosphate plated to prevent rust. “We’ve learned from examining original cars that they have the ‘X’ on them,” says Scott.“ The cap is a black NOS Delco Patent Pending cap. Some caps have the patent number instead of the Patent Pending, but we’re not real sure when the changeover happened. The general consensus is that a ’65 would have Patent Pending instead of the patent number.”

The coil is a standard Pontiac 214 coil, painted brown to match its Bakelite top. The bracket and bolts are plated with silver cad. The small bolt is where the passenger-side ground strap will attach.
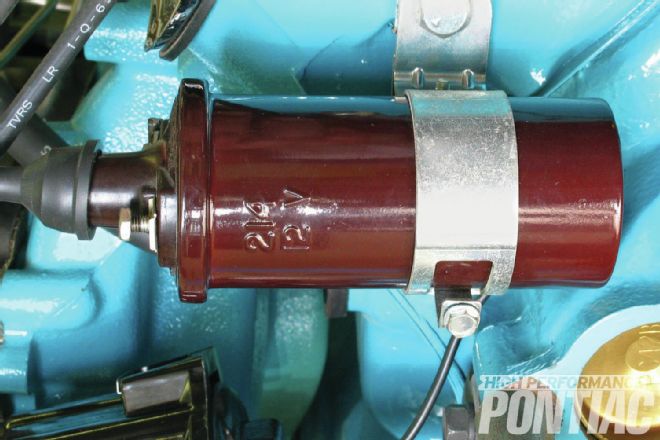

The starter bracket and can are semi-gloss black with overspray extending onto the aluminum housing. The solenoid can above the starter is also semi-gloss black. To ensure a good electrical contact, the contact edge of the starter lead is unpainted, as is the front of the solenoid with all of its electrical contacts. Visible in the side of the block is a brass plug for the water jacket. It’s unpainted now while the engine is test run, but it will be painted engine blue before the engine is installed.
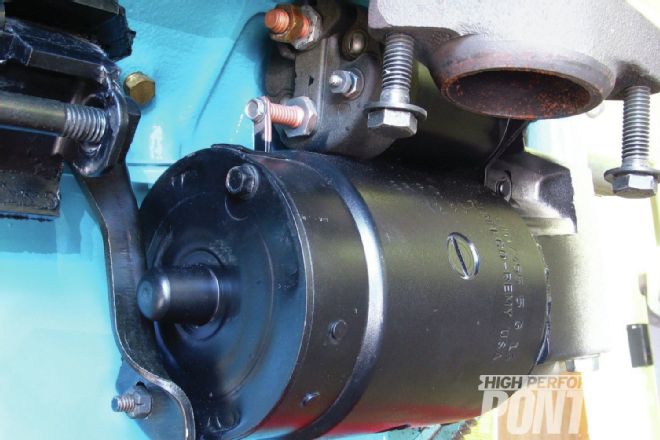

Bolts are missing at both ends of the exhaust manifold. This is intentional. “The manifold is machined for six bolts, but they only put in four,” says Scott. “Whether they had cracking issues, I don’t know, but ultimately they left two bolts out of the ends of the manifold on these ’65 cars to allow it to expand and contract a little easier.” The remaining bolt is hardened with a black finish, and the bolts at the front and rear cylinders have lock tabs to prevent loosening. Scott doesn’t bend the tabs over until the car is ready for delivery in case the manifolds should need to come off.
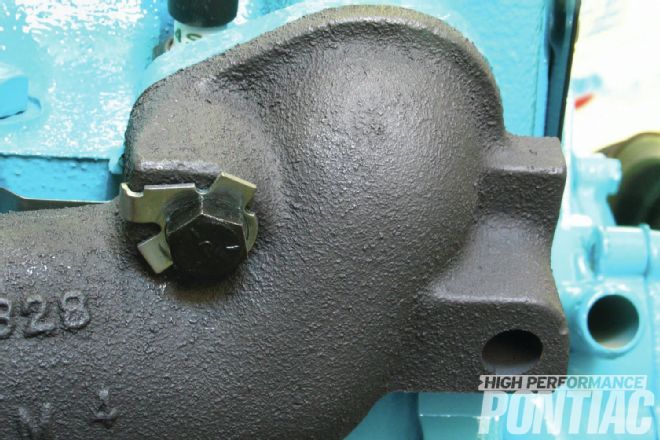

These exhaust manifolds are pristine castings from a California donor car, so the surface is smooth and consistent, free of craters and pock marks from heavy rust. They use a common metal gasket between the manifold and head. Rather than the usual DIY manifold coatings, Scott prefers a dark-gray ceramic coating outside that approximates the look of bare cast-iron, and a second coating inside the manifold to reduce the heat migrating into the engine that discolors the exhaust ports, a common problem among Pontiac V-8s. Scott has another technique to prevent excessive heat in the engine. “The trick that we do,” he says, “is to take the center out of the thermostat so that coolant is constantly flowing, just as if the thermostat was wide open. You have to have it in there so that you’re restricting the flow a bit. Then I cut the valve out of the heat riser in the passenger-side exhaust manifold so that the heat is never dammed up inside the engine. This helps keep the exhaust ports from burning and discoloring. This engine has been run for an hour on my test stand, and that’s how it looks still. It’ll start turning a little bit as you drive it, but it’ll never get black and crispy like they would otherwise.”
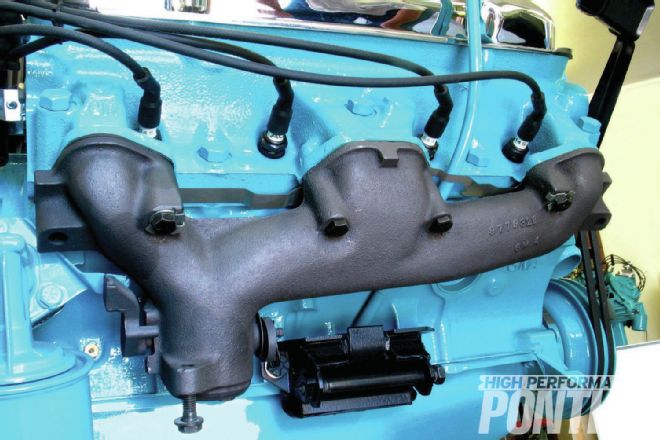

Located on the right-side exhaust manifold, down low just above the exhaust-pipe connection, is the heat riser, a temperature-activated valve that diverts hot exhaust gas through a passage beneath the carburetor in the intake manifold to aid in cold starts and warm-up. Once the engine heats up, the valve is supposed to open and let exhaust flow freely. Because it’s essentially an obstruction in the exhaust path, Scott modifies it for better performance, and to make sure it can’t malfunction and stick closed. “I leave the rod, weight, and spring in, and they will function correctly, but there’s no butterfly valve in there, so it never dams up the heat in the engine. The engine’s going to warm up slower, but I’m willing to sacrifice that to keep the paint looking nice.” The stop tab on the bracket is wrapped in a layer of asbestos and is painted engine color. The counterweight gets the same finish as the exhaust manifold.
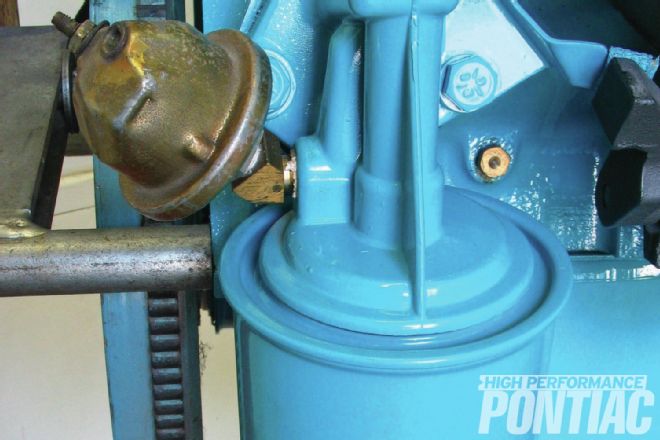
“The oil filter is a PF7, which is what the engines came with originally,” says Scott. “It has a little nut on the bottom, and it’s mid-’60s vintage out of an original box. I painted it engine blue as it would have been during assembly of a new vehicle.” Up above the oil filter is the gold oil-pressure sender mounted on a 45-degree adapter, used with the gauge on the optional Rally dash. Cars without the gauge used a simple warning light on the dash, triggered by a smaller switch at the oil filter, and mounted without the 45-degree adapter.


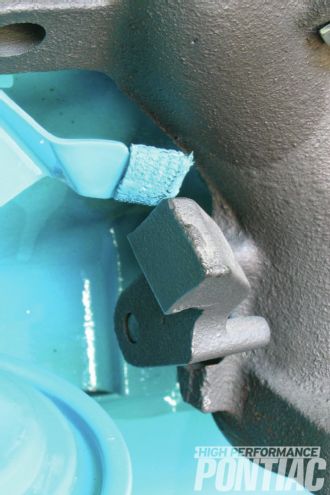
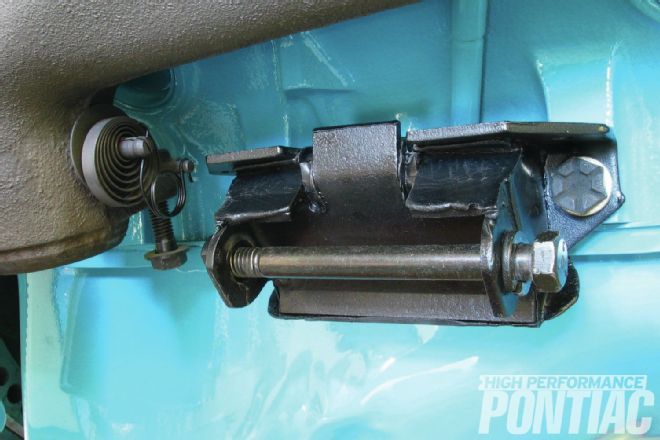
Coiled around the heat-riser shaft is the thermal spring, which opens the valve as the engine warms. A smaller wire anti-rattle spring tensions the heat-riser shaft and is almost always missing from GTOs. The motor mounts are originals from the low-mile California parts car. Hardened bolts with phosphate finish attach the mounts to the block. Silver-zinc washers are used here.

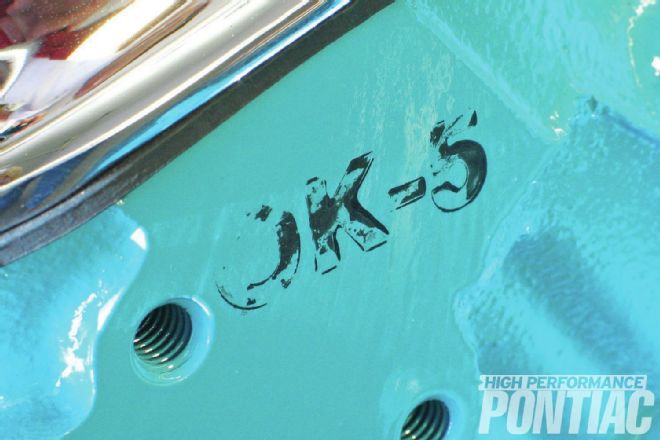
At the front of the right-side cylinder head is “OK-5,” a general stamp of approval for the engine assembly. Numbers may vary depending on which inspector stamped the engine. Scott re-created the original stamp and stamped the front of the passenger-side cylinder head in the correct location. This highly detailed ’65 389 Tri-Power gets our seal of approval, too.

Masters City Corvette Parts
(706) 860-9047
Supercar Specialties
Woodruff Carburetor Restoration
(330) 799-9479