

When most of us think of trans brakes, Super Comp dragsters and other race-only quarter-milers come to mind. But if your street-and-strip ride has a traction surplus, a trans brake may be what you need. The age-old practice of foot-braking the torque converter by applying the brakes while increasing throttle is only marginally effective. Eventually engine torque overcomes the ability of the wheel brakes to resist axleshaft rotation, and the tires either break traction and spin or the car creeps forward before you want it to. Either way, full stall speed is not reached. When the light turns green, the engine is farther from peak torque than it could be, and performance suffers.
Trans brakes handily address this problem by uncovering every last bit of stall the converter has to offer so the engine is closer to its torque peak. That means there's more grunt available to get you moving as quickly as possible when the race starts. As we know, the initial rate of acceleration from rest plays a vital role in cutting e.t. Trans-brake users typically see a 1- to 2-tenth reduction in the time it takes to reach the 60-foot mark. If that seems inconsequential, remember a tenth on the starting line is roughly equal to a car length by the finish line.
What Is a Trans Brake?
Available for most popular automatic transmission applications from companies like TCI for between $400 and $500, a trans-brake conversion consists of a few (reversible) case modifications and a specially modified valve body that's equipped with an electric solenoid. A driver-operated pushbutton triggers the solenoid to move a shuttle valve, causing the transmission's hydraulic circuitry to engage First and Reverse gears at the same time. If this sounds like a recipe for self-destruction, remember the car is not in motion when the activation button is depressed. With the transmission input-shaft effectively locked, the driver then mashes the accelerator pedal to the floor, giving the torque converter no option other than to slip until its absolute stall speed is reached. When the light turns green, the driver releases the activation button and the car explodes off the line. Once moving, the driver upshifts the transmission in the usual way.
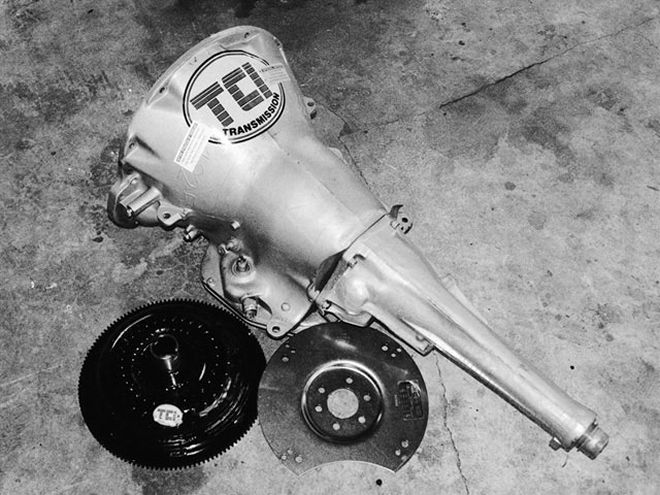 TCI-supplied goodies include: a full-manual, trans-brake 727 Torqueflite (PN 112700); a 10-inch Super Street Fighter torque converter (PN 142222); an SFI-certified, externally balanced flexplate (PN 102360); and (not shown) a reverse pattern shifter (PN 148000); a 6-foot, 2-inch stroke shift cable (PN 840600); and a spiral-cord activation switch (PN 388400).
TCI-supplied goodies include: a full-manual, trans-brake 727 Torqueflite (PN 112700); a 10-inch Super Street Fighter torque converter (PN 142222); an SFI-certified, externally balanced flexplate (PN 102360); and (not shown) a reverse pattern shifter (PN 148000); a 6-foot, 2-inch stroke shift cable (PN 840600); and a spiral-cord activation switch (PN 388400).
Should trans-brake users be worried that the engine might over-rev and break when they mash the gas with the trans-brake button depressed? No. Although holding the pedal on the floor when the car isn't moving yet goes against every hot rodder's base instincts, the churning torque converter safely maintains enough resistance to limit engine speed. But for peace of mind, many users install a multi-step rev-limiter just in case, and to fine-tune the launch rpm to match track conditions.
Things to Consider
While a trans brake will typically produce a higher stall speed than foot-braking alone, it won't transform a low-stall OE stocker into a full race converter, so don't look for miracles. TCI tells customers to move up to a trans brake only after they've already installed a torque converter that is well suited to their vehicle combination (weight, camshaft, gear ratio, traction potential, and so on). The best plan is to select a torque converter that, with the trans brake engaged, allows the motor to flash to within 200 rpm of its torque peak. There are plenty of chassis dynos in the land these days, so peak torque data is easily obtained for a modest investment.
Also, because trans-brake use requires modified staging and launch techniques on the already nerve-wracking launch pad, make the job as easy as possible. TCI suggests mounting the activation switch on the shift handle or steering wheel. With a little practice, it soon becomes second nature and you'll discover that better reaction times are possible thanks to the consistent launch rpm versus the less repeatable method of pedal-juggling the launch stall speed. Also, most people are able to release a fingertip button more quickly than they can move their feet to lift the brake pedal and mash the gas, another reaction time benefit made possible by the trans brake.
Most importantly, a trans brake will likely subject the rear tires and suspension to increased torque. Earlier we used the term "traction surplus." It describes the desirable condition in which full engine power can be applied to the pavement without tire slip. Installing a trans brake on a car that is already at its traction limit can cause the tires to spin and reduce performance. Buy bigger slicks!
Let's Try It Out
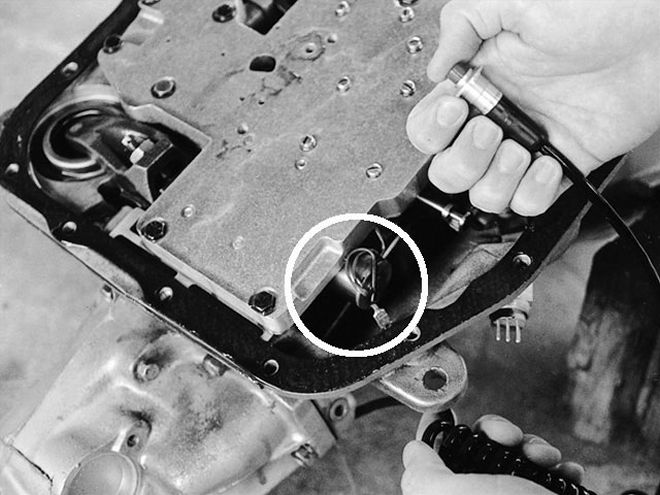 The specially cast and machined TCI trans-brake valve body is available separately so it can be added to your existing transmission. The electric trans-brake solenoid (circled) directs hydraulic pressure to engage Reverse and First whenever the microswitch button is depressed.
The specially cast and machined TCI trans-brake valve body is available separately so it can be added to your existing transmission. The electric trans-brake solenoid (circled) directs hydraulic pressure to engage Reverse and First whenever the microswitch button is depressed.
To see what it all means, we sourced a TCI trans-brake transmission and converter package and plugged the whole works into a 4.30-geared 2,980-pound Duster powered by a dyno-proven 360 small-block (402 hp at 5,700; 409 lb-ft at 4,400) and hit the Irwindale, California, eighth-mile strip. Some readers may remember the car as our Hyper-Pak Slant Six test mule from the Dec. '00 issue. The leaning tower of power is in another car now, but a V-8 conversion kit and adjustable torque strap from Schumacher Creative Services accepts the bent eight without forcing the hassle of swapping the six-cylinder K-frame for a V-8 unit. It's a Mopar thing.
With plenty of VHT on the track and a hot burnout, the converter foot-braked to 3,400 rpm before the 27x10.00-15 slicks began to churn. On the pedal, the best run was a 7.578 at 90.27 (approximately equal to 11.88 at 114 on a quarter-mile track) with an impressive 1.670 60-foot time. Then we tested the trans brake. With the button depressed and the gas pedal flat on the floor, the converter stalled 1,600 rpm higher at 5,000. The best pass was a 7.593 at 90.37 with a 1.685 60-foot time.
Shouldn't the extra stall speed produce quicker 60-foot times? Yes, but in our case the added stall put the engine speed 600 rpm above peak torque output. The brake-pedal stall speed of 3,400 rpm put the engine 1,000 rpm under peak torque output, a better place to be since the torque curve is still rising rather than falling when the car begins to move. The near miss on the torque curve was enough to decrease acceleration to the 60-foot mark by 0.015 second. See what we mean about choosing the right converter? A slightly lower stall speed would have reversed the outcome, and quicker 60-foot times would surely result.