Fans of the Ford Windsor small-block are probably more limited in the horsepower department than fans of any other small-block engine family. It is not for a lack of desire or ingenuity on their part either—there are just too many obstacles in the strength and airflow areas to overcome. That might sound strange in an era where small-block Fords are plentiful and can avail themselves of many cylinder heads, induction choices, and aftermarket blocks, but put in historical perspective, the need for those improved parts becomes clearer.
Conceived originally as an entry-level V-8 for the midsized Fairlane in 1962, the lightweight 221ci Windsor V-8 had just 145 hp. It did the job wonderfully; it was light, fuel efficient, and inexpensive to produce. The overall Windsor architecture was so good, in fact, that it outlived its replacement, the 335-series engine family (351 Cleveland, 400M). But unlike the small-block Chevy that was introduced seven years before, the Windsor was not intended from the get-go as a high-performance mill. By comparison, it had less of everything—cubic inches, airflow, and strength. As a result, the Windsor rapidly grew in size to 260, 289, 302, and eventually 351 ci. Unfortunately, most of the strength areas in the block that needed to be addressed in order to make modern-day hot rodding power were not sufficiently improved.
Blue Oval fans who step up to the plate to build big power in the Windsor format often get burned by the production block, which is common in short-deck 8.2-inch (302ci, aka 5.0-liter) and tall-deck 9.5-inch (351W) versions. Today's wide selection of free-flowing Windsor cylinder heads, big intakes, stroker rotating assemblies, supercharger kits, and healthy camshafts are practically a guarantee that a production-based block is going to fail at or near the 600hp threshold.
Those failures come not from one source, but several, depending on the steps that have been taken. For instance, head gasket failure is common due to the cylinders having a thin-wall construction and to the cylinders having only four bolts per cylinder instead of five. More clamping load with beefier fasteners and O-ring seals in the block or cylinder head area are common solutions to retaining combustion pressure within the block, but this arises in another problem—cracked blocks. The Windsor block's legacy as a lightweight and economical casting is therefore problematic, as several areas cannot be effectively bandaged at a reasonable cost.
Over the years, aftermarket manufacturers have satisfied the need for a stronger Windsor block, answering the call with both 8.2- and 9.5-inch deck-height versions. Racers and street enthusiasts can now breathe easier with Ford Racing's Boss 302 and Boss 351 blocks, which have added significant amounts of strength to the cylinder walls, pan rails, cam tunnel, and main webbing, with a further improvement to the Boss 351 by means of a 2.75-inch (Cleveland) main journal diameter. But all that comes at the price of 100 extra pounds over the nose of the car. The solution? Take a page right out of the late-model playbook—go aluminum.
When it comes to building a car that handles, putting an extra 100 pounds high and far forward creates more problems than the extra power solves. (Highlighting the mass bogey, Ford thought it was enough of an issue that they created the in-between 9.2-inch deck-height racing block just to lower the Windsor's center of gravity by .3 inch.) The ideal situation would be to create a block that affords all of the strength of a beefy race block while adding none of the weight. To that end, Ford Racing created the high-strength M-6010-Z351 aluminum block. At around $3,479.95 from Summit Racing, the Z351 block has a 351-sized 9.5-inch deck height with enough space to swallow strokes to 4.25 inches and bores up to 4.125 inches. Plug those numbers into the handy displacement calculator and you get 454 cubes of badass small-block Ford—and plenty of revenge against the big-block Chevy of the same size.
The Z351 aluminum 351W block offers the Ford man a no-compromise foundation for any race or street high-performance powerplant where low mass is a premium. And while other aftermarket manufacturers have ventured into the rarefied territory of all-aluminum Windsor-based blocks at twice the price and more, none of them have made it remotely affordable like the folks at Ford Racing.
In the coming months, we will be building a 454ci small-block Windsor with this Ford Racing Z351 block as its foundation. The goal is to make 700-plus horsepower on pump gas in a wet sump configuration that will be installed in a road-race–ready street-legal 1965 Mustang coupe. Sharp readers will remember that we built an all-aluminum 438ci dry-sump "Clevor" (Windsor block with Cleveland-style heads) for the Project Max Effort 1967 Cougar ("Street Cup," Oct. 2011), which made 710 hp on pump gas. In order to one-up our own work, we'll need more cubes, more airflow, and more cam without giving up on the 91-octane pump gas. To that end, we're going the full monty with 454 cubes, a solid-roller cam, and a set of Trick Flow High-Port 240 CNC heads. We hope to have all the details of the short-block buildup in our December issue. In the time being, check out all the cool details big and small inside the Ford Racing Z351!
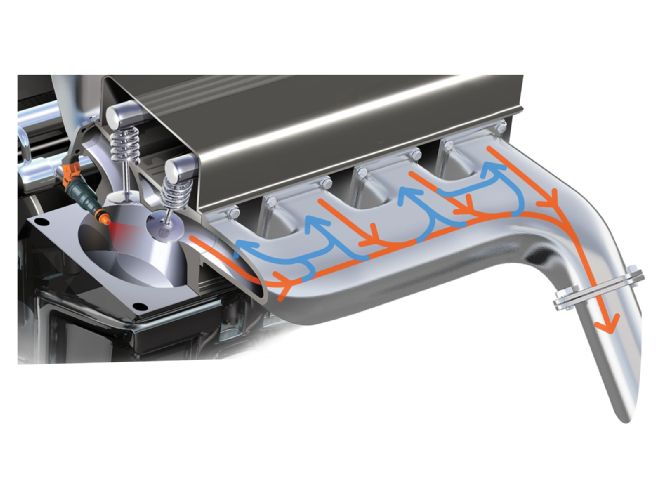
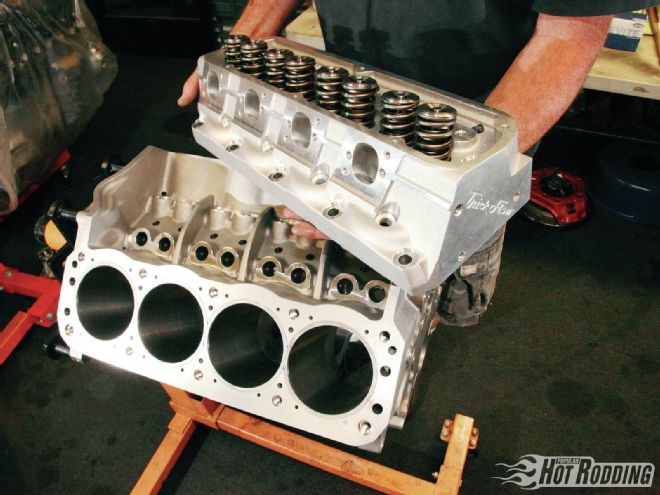 Our need for the strength and displacement provided by the Ford Racing Z351 block will become even more apparent when we mate it to a pair of deep-breathing Trick Flow Specialties (TFS) High-Port 240 CNC heads. TFS cut its teeth on small-block Ford performance 25 years ago, and they remain on the cutting edge of small-block Ford power today; these heads are capable of delivering enough airflow to produce well over 700 hp, and that’s our bogey.
Our need for the strength and displacement provided by the Ford Racing Z351 block will become even more apparent when we mate it to a pair of deep-breathing Trick Flow Specialties (TFS) High-Port 240 CNC heads. TFS cut its teeth on small-block Ford performance 25 years ago, and they remain on the cutting edge of small-block Ford power today; these heads are capable of delivering enough airflow to produce well over 700 hp, and that’s our bogey.
BY THE NUMBERS
Ford Racing M-6010-Z351 Block
High-strength aluminum block, 356-T6 grade aluminum
Splayed 4-bolt steel billet main caps on 2, 3, and 4; 2-bolt billet steel main caps on 1 and 5
4.110- to 4.115-inch bore as delivered, cast-iron sleeves, 4.125-inch final bore
9.5-inch deck height, accepts small-block timing chain, timing chain cover, and oil pump
2.75-inch (351C) main journal diameter, 2.9415- to 2.9425-inch diameter finished main bearing bore
Lifter bores finished .8753 to .8768 inch
2.2032- to 2.2052-inch diameter cam bearing bores; uses cam bearings (PN M-6261-J351)
Maximum stroke 4.250 inches
Wet sump oiling system
Weighs approximately 110 pounds