

Brake technology has progressed over the years, and we like to keep abreast of the developments and trends related to racing brake systems. A popular format is to send out questions to brake experts and then relay their comments to you. So read on to learn some interesting tales about how brakes can improve your performance.
We developed a list of 10 common questions racers might have concerning their brake systems and contacted representatives of leading brake companies. They are as follows: Ken Gordon, AP Brakes; Jeff Smallwood, Hawk Brakes; Todd Howerton, Outlaw Brakes; and Carl Bush, Wilwood Engineering. Being a chassis setup guy, I had no idea there was so much to know about brakes. Learning, for me, is always a lot of fun, so here we go.
1. How do I choose the proper brake pads for my type of racing?
AP: Generally, racers are aware of the setups and parts being used by the competitors who are the most successful. When starting out in a new class or in a new car, observing what the winners run is a time-honored way to get close right off the bat.
Hawk: A good start is to become familiar with your brake system temperatures. At that point, a better decision can be made when selecting a range of friction compounds that meet the criteria. From there, it's a matter of determining a performance level that suits the individual driver's needs regarding initial bite, fade resistance, consistency, and so on.
Outlaw: The pads need to suit the type of racing and should be tailored to the driver's style. The more feedback that can be obtained from the driver, the more accurately the crew will be able to select the proper pads. It is difficult to say that any particular set will work for all drivers in a single class.
Wilwood: Temperature range is generally the first consideration when selecting a pad compound. The pads must be responsive and capable of resisting fade at the temperatures realized during competition. Wear rate is also a key.
The pads must be able to sur-vive the length of the event. Once the selection process has been narrowed to compounds that have the proper temperature range and wear rate, attention can be given to overall response and stopping power.
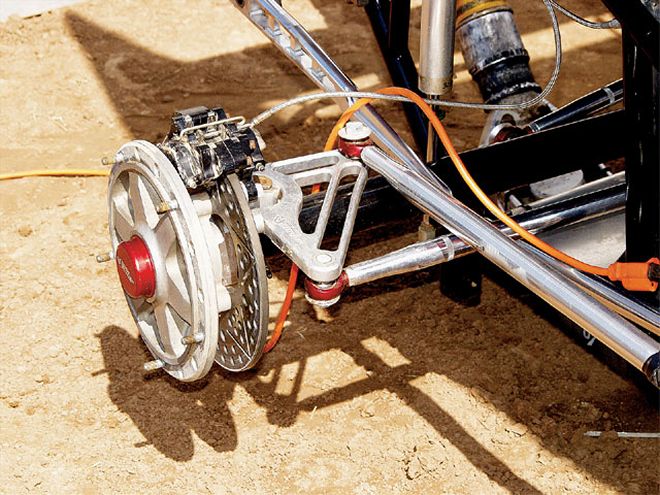 The choice of which brakes to use entirely depends on the type of car and the surface on which you will be racing. For Sprint Cars, the front brakes should match the tire size-less tire, less brake.
The choice of which brakes to use entirely depends on the type of car and the surface on which you will be racing. For Sprint Cars, the front brakes should match the tire size-less tire, less brake.
2. How do I choose the proper brakes for the two different types of racing, dirt and asphalt? Is there a difference?
AP: Yes, there are huge differences, as each type of racing calls for different brake types. Ask the manufacturers for information on their recommendations for your type of racing. They have a big interest in you doing well, so they will not steer you wrong.
Hawk: It's important to be sure the pad material is designed to be used in the given temperature or performance environment. Many materials provide performance over a wide range of temperatures, while other materials will only perform as intended when used in specific temperature ranges.
Outlaw: Brakes for dirt and asphalt are very different, just as chassis setup involving the shocks and springs are different for each. Many factors, such as sanctioning requirements, the car's body type (open wheel or full body), the track's surface (dirt or asphalt), the type of track (track size, flat or banked), and the driver's style determine the proper brakes. We offer baseline recommendations, but we may also be able to work with individual teams to fine-tune the systems with proper information on their current system and how it is performing for them.
Wilwood: Asphalt racing usually generates consistently longer and higher heat cycles than dirt racing. That normally translates into the need for heavier rotors and pad compounds with higher heat ranges for competition. But the bottom line on pad and rotor selection, regardless of where the vehicle is raced, is based on two key items:
1.Will the pads last an entire event without fading or completely wearing away?
2.Are the rotors heavy enough to last the entire event while keeping the pads in a manageable temperature range?
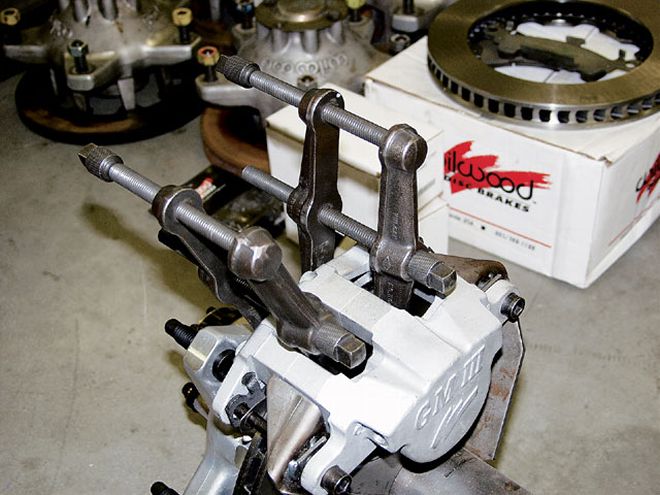
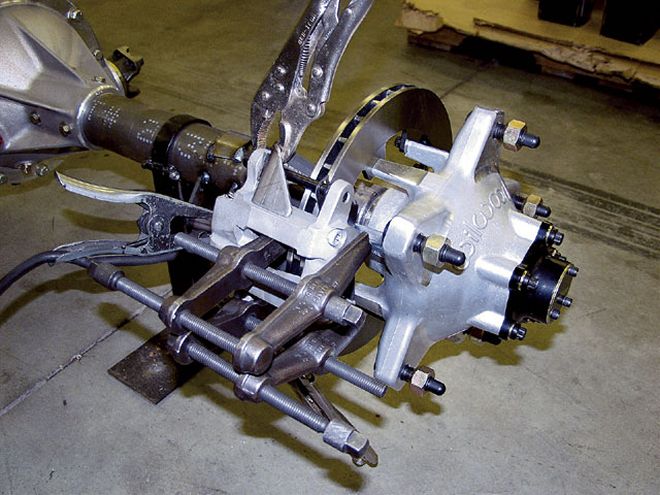 When mounting the caliper to the spindle, care must be taken to properly align the two. On our Late Model car, we clamped the caliper to the rotor using a spacer to provide proper clearance for the brake pad.
When mounting the caliper to the spindle, care must be taken to properly align the two. On our Late Model car, we clamped the caliper to the rotor using a spacer to provide proper clearance for the brake pad.
3. What are some common problem areas during the installation of brake calipers and pads?
AP: By far the number-one error in caliper installation is having the caliper too low on the disc. The caliper should be square and true in alignment with the disc, and there must be at least 0.080 inch of clearance [0.100 inch is better] between the outside diameter of the disc and the inside of the caliper disc pathway. The disc expands when hot, and the diameter increases. The caliper will overheat and fail if the disc rubs the inside of the caliper.
Hawk: Not properly bleeding air from the system after installation is common and can create an inaccurate sense of brake performance and effectiveness.
Outlaw: The calipers need to be mounted square and parallel to the rotor. Check the rotor for runout and then make sure the caliper is mounted properly over center. Also, make sure the caliper is mounted square to the centerline, which may require tweaking of the spindle mounts. The calipers should also be mounted so that the pads sit flush to 0.020 inch above the outer edge of the rotor when they are installed. This allows for rotor growth, maximizes the use of the rotor surface, and equalizes the temps on the rotor edge to help avoid unnecessary warping.
Wilwood: The calipers must be aligned laterally over the rotor. They must be square and parallel, with the rotor centered evenly between pistons. The caliper must also be in proper radial alignment, with the outside radius of the pad matched against the outside radius of the rotor. Lateral alignment can usually be corrected with shims between the caliper lugs and mount bracket. Calipers must always be mounted with the bleed screws on top. Otherwise, they cannot be properly bled.
 We use different-size master cylinders to vary the braking force generated. Here, the two cylinders on the left represent the brakes, front and rear. The cylinder on the left, for the front brakes, is smaller than the one for the rear brakes (look just under the bleeders to see the piston cast size). This provides more stopping power for the front brakes on this asphalt car, which is necessary.
We use different-size master cylinders to vary the braking force generated. Here, the two cylinders on the left represent the brakes, front and rear. The cylinder on the left, for the front brakes, is smaller than the one for the rear brakes (look just under the bleeders to see the piston cast size). This provides more stopping power for the front brakes on this asphalt car, which is necessary.
4. How do I properly break in my new pads?
AP: The simple answer is to follow the pad manufacturer's procedure to the letter. Generally, these instructions are in the box of pads, and the manufacturer has done a lot of testing to determine the best procedure for its pads.
Hawk: Most friction manufacturers recommend similar procedures, yet, unfortunately, many racers do not accomplish the most important part of the bedding process, and that's a very slow heat buildup over an extended amount of time followed by a complete cool down. It's highly advisable to follow the manufacturer's recommendation very closely to ensure you get the intended performance from your pads.
Outlaw: Pad break-in may vary depending on the pads being used, but it is generally noted that new pads should be bedded on rotors that have been previously used with the same type of pad. The same applies to rotors. It is a good idea to have your spare pads and rotors bedded, and keep a matched set for that time of need.
Wilwood: The first laps on new pads and rotors are the most critical in their life cycle. Failure to properly bed them can not only result in poor performance, but also irreversible damage to the pads and rotors.
Make a series of six to eight light stops, with a 10-15-second complete release between each stop. Proceed to a series of three to four laps with six to eight medium stops from a slightly higher speed. Proceed further to full-speed laps, making six to eight hard stops to bring the brakes up to real operating temperatures. Then, back off and make a few cool-down laps, using the brakes as little as possible if not at all.
The warm-up cycle involves the driver pushing the brake pedal to make full contact between the brake pads and rotor, then full release of all pressure on the brake pedal to properly warm the parts and bed them in. Open-track practice days present the best opportunity for pad and rotor bedding. It's a good idea to take along a spare set of pads and rotors and bed them during the open-track time.
5. What are some common solutions to bias problems?
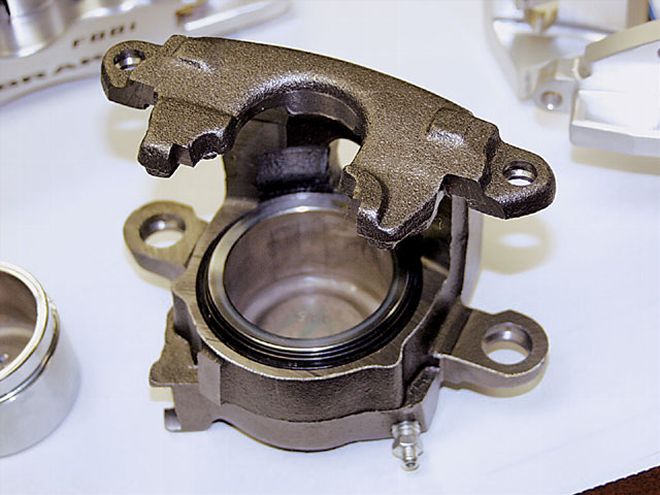 To influence brake bias, we can also install calipers with different-size pistons. Larger pistons generate larger forces. Smaller master cylinders also produce greater hydraulic force.
To influence brake bias, we can also install calipers with different-size pistons. Larger pistons generate larger forces. Smaller master cylinders also produce greater hydraulic force.
AP: 99 percent of "bias problems" (i.e., too much front or too much rear brake) are not in fact brake problems; they are chassis problems. After the correct springs, shocks, alignment, antiroll bar, and corner weights are achieved, it can be determined if a bias adjustment is needed.
The bias bar found in many race cars is not a fundamental tool for adjusting brake bias. Rather, it allows the driver a very small range of brake bias adjustment during the race in order to help the car turn less or more under braking.
Hawk: As related to friction materials, proper bias control starts with selecting pads that are designed to perform consistently throughout the range of temperatures created in the individual racing environment.
Outlaw: The use of different caliper piston sizes front and rear, different master cylinder sizes front and rear, different grip value pads at the front and rear, the use of proportioning valves, and using brake balance adjusters are all accepted ways to solve bias problems.
Wilwood: First, it should be stated that before considering any major changes to the brake system to affect the bias, there should be some degree of certainty that the overall chassis setup with springs, shocks, weight percentages, tire stagger, and the like are in a good workable range.
The solutions to bias problems are as varied as the number of brake parts on the car. With the exception of fluid, or a single master cylinder brake pedal, every other component in the brake system can somehow affect bias.
The question to which bias solution best applies then becomes part of what parts on the car can actually be changed. Adjustments to the balance bar or proportioning valve can really only be used to make fine incremental adjustments of the bias to improve handling during competition. If there is not enough adjustment range on either part to adjust for track conditions, fuel load changes, or tire wear during the race, then the static configuration of the car must be re-evaluated.
All of the available options must then be considered to determine whether a master cylinder change, a caliper piston size change, a rotor diameter change, or a pad compound change is the next best option to put the car into a favorable static bias range that allows good handling and effective use of the balance bar or proportioning valve on the track.
6. Are pressure gauges useful to monitor brake bias?
AP: Yes. The types of pressure gauges used as tools by race mechanics are good diagnostic tools if used during the installation and set up of the brake system to check pressure at the calipers. They should never be mounted permanently in the car or used during racing.
Hawk: Yes, and even more important is using a pressure gauge to determine that each caliper is receiving proper pressure, as an imbalance of pressure at the caliper can often lead to an unstable braking feel.
Outlaw: Monitoring pressures while driving/braking is very difficult to do. The in-dash gauges also make the system more difficult to bleed and maintain because of the additional fittings and lines. Some people mention a softer pedal after the addition of the gauges, which could be due to difficulty in bleeding, pressure being absorbed to activate the gauge, or the additional lines and fittings.
We recommend a pair of gauges that can be screwed into the bleeders of the different circuits of the brake system in the shop. The set up can be done in the shop, where you have time to monitor the pressures, and then full attention can be used while racing.
Wilwood: Pressure gauges are essential to accurate set up and evaluation of the brake system. Pressure gauges are the only tools that can provide accurate analysis of balance bar or proportioning valve settings. It's generally best to take pressure readings at the calipers. Analyzing the pressure data against on-track performance can also help determine whether and how a component change may affect the static bias balance.
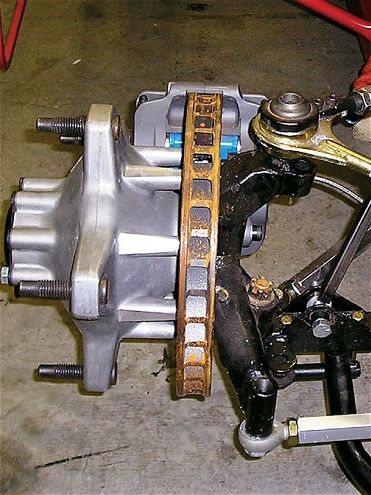 You should check the pad thickness often to ensure a sufficient amount of material for the next race. Here, we can see the blue pads easily once the wheel has been removed. Also, check for unusual wear and large cracks in the rotor. Smaller cracks are normal and expected.
You should check the pad thickness often to ensure a sufficient amount of material for the next race. Here, we can see the blue pads easily once the wheel has been removed. Also, check for unusual wear and large cracks in the rotor. Smaller cracks are normal and expected.
7. How long do pads last, and how do I know when to change them?
AP: A wear rate can be determined for the pads on your car at your track. Pads should be replaced when one of two things happens:
1.Your brakes are working well, but the pedal travel has increased due to the pad material wearing away to the point that you need to apply the pedal a tiny bit earlier in order to get the braking effect you need when you need it.
2.You check the pads after each race, and they have worn down to a friction material thickness of 0.100 inch. Remember that pads often wear unevenly, so measure them at the thinnest place and check inners and outers. Never put a new pad in with an older one.
Hawk: If properly bedded, compounds will maintain effectiveness regardless of how much material is worn away. The bigger issue is the caliper pistons must travel farther as the pad loses thickness, causing a delay in effectiveness and a longer pedal stroke.
Wilwood: There's no real way to predict how long a pad will last in race conditions. There are far too many variables. Brake pads should be inspected after every event. If there is no longer enough material on the pads to finish the next event, they obviously need to be replaced.
8. What kinds of pad material are available?
AP: The good news is there are at least 30 great pad compounds available these days. The bad news is there are at least 30 great pad compounds available these days. Generally, all pads supplied by all the front-line, well-known suppliers are really good quality pads. There are some significant differences in characteristics, though.
Hawk: We manufacture a wide variety of friction materials, many designed for a specific racing type, rotor material, and/or performance value. We spend a lot of time evaluating the performance needs for different racing environments and design our pads to meet and/or exceed these requirements.
Wilwood: Friction technology is constantly evolving and there are lots of materials being used to produce good friction. For the racer, it's not really important to know what's in the pad, but it is important to know the performance characteristics and what a particular pad material will do for him on the track.
9. For reduced braking power, is it better to use smaller pads at the rear or different-size calipers?
AP: Different-size calipers will be needed to reduce rear braking. However, you should always use as much rear brake as possible. The reason is that you only have four small tire contact patches. The more you can make all your contact patches share the job of gripping the track for turning and braking, the faster your car will go. If you can get 10 percent more of your total braking from the rear than the next guy, at the end of the 200-lapper, his front brakes will be toast, and you will be cruising to victory.
Hawk: Regardless of which end of the car you are wanting to control, if reduced braking effectiveness is desired, it can be achieved by using calipers with smaller piston sizes. Also effective is selecting a friction material with the appropriate performance values.
Outlaw: I assume you are referencing an asphalt car, as dirt cars generally require more rear brake. Using smaller pads will require a smaller caliper because the pads are sized to the caliper. Pad compounds can be changed to adjust braking power as well as proportioning and master cylinder or caliper piston size.
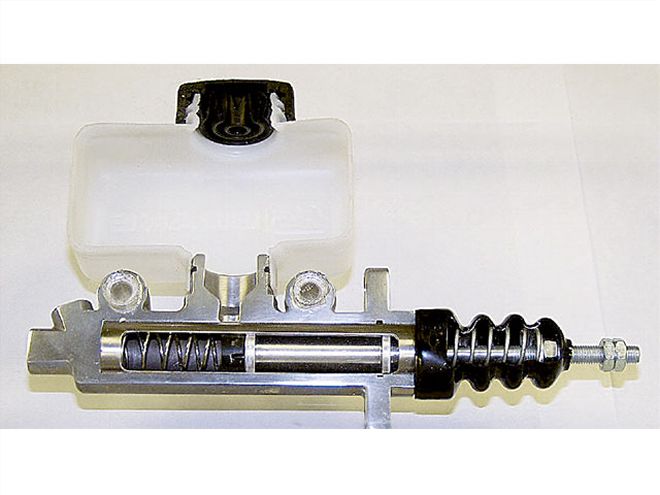 The piston size in the master cylinder affects the amount of fluid pressure related to foot-pedal pressure. The same foot pressure will generate more line pressure when a smaller piston is used than when a larger one is used. This way we can regulate and alter the braking forces at each end of the car when the error in bias is outside the normal adjustment range for bias bars and pressure regulators.
The piston size in the master cylinder affects the amount of fluid pressure related to foot-pedal pressure. The same foot pressure will generate more line pressure when a smaller piston is used than when a larger one is used. This way we can regulate and alter the braking forces at each end of the car when the error in bias is outside the normal adjustment range for bias bars and pressure regulators.
Wilwood: Changing to a smaller caliper piston size or using a larger-bore rear master cylinder are the only real ways to measurably change the static bias in the car. Smaller pads may run hotter and fade or wear out faster, but they will not affect bias. The only pad change that should be considered as an adjustment to the dynamic rear bias is the use of a compound with a different friction value at temperature. Racers should never modify a brake pad in an attempt to achieve some perceived performance advantage.
10. How do I know when to use a balance bar or when a brake pressure regulator will do?
AP: Easy-if the rules allow a balance bar, always use a balance bar. Never use a pressure regulator. If the rules do not allow a bias bar, a pressure regulator in the line to the rear brakes will allow the rear brakes to be reduced somewhat. If you have the choice, use a balance bar; it is a much better and more useful tool.
Hawk: In most cases, the balance bar should be used to maintain or stabilize braking effectiveness front to rear. Pressure regulators are helpful to reduce the braking effectiveness of an individual corner of the car.
Outlaw: This depends on what the rules and regulations for the class require or allow. The balance bar should be set so it is in the middle of adjustment and should not be adjusted more than one to two turns in either direction.
Wilwood: If the car is not equipped with a balance bar pedal, or if the desired brake adjustment is not within the range of balance bar functions, then a proportioning valve can be used. The user must remember that all proportioning valve settings have a minimum start-up pressure and may not affect proportioning at lower pressures. The adjustable balance bar provides consistent bias change regardless of pedal effort and line pressure. If the car is equipped with a balance bar adjuster, it is generally the first tuning choice.
Conclusion: Now that we have learned a few things about brakes, we might have even more unanswered questions. You might want to develop a relationship with one of these brake companies. Contact your brake professional so that you can custom-design your brake system to suit your individual needs.
Remember that brake tuning is best done after the setup issues have been addressed and sorted out. Then you can fine-tune the entry characteristics for your car.